What is Cost-volume-profit(CVP) analysis?
Cost volume-profit analysis
Concept of cost-volume-profit analysis
The top dog objective of a trace of piece of employment concern is to maximize profit. There are unlike too internal too external factors which touching on profit. Profit is maximum zed amongst the decrease inward cost too increment inward revenue i.e. sales. The costs of products are determined yesteryear the purchase of raw materials too other manufacturing too operational activities. Similarly, sales are theme on selling price, need too character of product, contest level, promotion too publicity etc. turn a profit planning is a role of selling toll per unit of measurement of product, variable cost associated amongst it a full fixed cost. In this way, the analysis of cost, book too turn a profit is essential to earn the target turn a profit too maximize it.
Cost- book turn a profit (CVP) analysis refers to the analysis betwixt cost too book of sales to examine their number on profit. It involves the formulation of the policies too strategies regarding the revenue too cost of an organization. CVP analysis is non confined to turn a profit making arrangement rather it is as of import to non-profit oriented organizations.
It attempts to supply answers to the next questions:
• What is the minimum degree of sales required to comprehend full cost too so as avoid loss?
• What sales book is necessary to earn a certainly degree or amount of profit?
• What volition hold upward the number of accuse is selling toll on profit?
• What volition hold upward number of changes inward cost on sales too profit?
• What volition hold upward the number on cost, book too turn a profit yesteryear the changes on production capacity too operational process?
In this way, CVP analysis is a tool of administration accounting to exhibit the human relationship betwixt components of turn a profit planning. Here, cost refers to variable too fixed cost. Te book refers to sales or revenue too turn a profit refers to the departure betwixt sales book too cost.
Proposes of cost –volume-profit analysis
The top dog objectives of CVP analysis are given below:
• To forecast to turn a profit yesteryear the analysis of cost too book of sales.
• To calculate intermission fifty-fifty point.
• To care preparing flexible budget.
• To exhibit the effects of the changes inward price, cost too profit.
• To approximate the sales book to earn a desired or expected profit.
• To mensurate the elements or factors that touching on profit.
• To select the best alternate for maximizing profit.
• To select the optimum production mix for production.
• To care to brand determination on manufacturing or buying.
Application of cost-volume-profit analysis
CVP analysis is an importance tool of managerial accenting. CVP analysis is used to brand a number of managerial decisions which are:
• Determine the break-even point.
• Control cost
• Make turn a profit planning
• Performance selling price
• Decide on buying or manufacturing
• Decide on profitable sales mix
• Measure the effects on turn a profit due to the changes inward selling price
• Maintain the desired profit
Assumptions of cost-volume-profit analysis
The analysis of cost-volume too turn a profit is based on the next assumptions:
• The costs are classified into fixed too variable costs.
• The selling toll remains unchanged irrespective of the book of sales.
• The per unit of measurement variable cost too the fixed costs ever rest the same.
• There is no alter inward production capacity too science or capacity of the workers.
• In instance of multi production companies, the sales mix remains the same.
• There is no departure betwixt the production too sales volume. It agency at that topographic point is no beingness opening too closing stock.
Contributions margin analysis
Meaning of contribution margin
The departure betwixt sales or revenue too variable cost is called contribution margin. In other words, it is the ease of sales afterwards convertible expenses. It is available to realized turn a profit afterwards recovering fixed expenses. The higher contributions margin is the indicator too so audio profitability position. Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 theatre suffers from loss which the contribution margin is lesser than the fixed cost. Thus, contributions margin analysis is useful to mensurate the turn a profit earning capacity of an capacity of an organization. The contribution margin is calculated inward the next way:
Total contribution margin (TCM)= full sales – full variable cost
Or
= fixed cost ± profit/ loss
Contribution margin per unit of measurement = selling toll per unit of measurement _ variable cost per unit of measurement (VCPU)
The ratio betwixt the contribution margin too sales is called contribution margin ration. Contribution margin ration is also called the turn a profit book ration. Higher contribution margin results inward higher turn a profit too vice versa. It tin sack hold upward increment yesteryear increasing the selling toll per u nit, decrease the variable cost per unit, switching the production to to a greater extent than profitable products etc.
Total contribution margin (TCM)= full sales – full variable cost
Or
= fixed cost ± profit/ loss
Contribution margin per unit of measurement = selling toll per unit of measurement _ variable cost per unit of measurement (VCPU)
The ratio betwixt the contribution margin too sales is called contribution margin ration. Contribution margin ration is also called the turn a profit book ration. Higher contribution margin results inward higher turn a profit too vice versa. It tin sack hold upward increment yesteryear increasing the selling toll per u nit, decrease the variable cost per unit, switching the production to to a greater extent than profitable products etc.
Contribution margin or turn a profit book ratio is calculated inward the next ways:
1. CM ration or P/V ratio on the footing of full = full contribution margin/ full sales
2. CM ration or P/V ratio on the footing of per unit of measurement = CMPU/SPPU
3. If sales, cost too turn a profit at ii unlike menstruation are given amongst constant fixed cost:
P/V ratio = differene inward turn a profit (profit)/ departure inward sales (sales)
P/V ratio = departure inward contribution margin/ departure inward sales
Variable cost book ratio or cost book ratio (V/V ratio)
It shows the human relationship betwixt variable cost too sales. The percent of variable cost on the footing of book is considered as variable cost book charge per unit of measurement or cost book ratio. The variable cost book ratio tin sack hold upward calculated yesteryear next way:
1. On the footing of total: V/V ratio= full variable cost/ full sales
2. On the footing of per unit: V/V ratio = CVPU/SPPU
Break-even dot analysis
Meaning of break-even point
Breakeven dot is the book of sales where at that topographic point is no loss. In other words, the book of sales inward which the full cost equals the full revenues is called the intermission fifty-fifty sales. Break fifty-fifty analysis is a managerial tool that shows the human relationship betwixt costs too turn a profit amongst sales volume.
Assumptions of break-even analysis
The analyses of break-even dot are based on the next assumptions:
• The costs are classified into fixed too variable costs.
• Variable cost remains constant inward per unit of measurement too fixed cost inward total.
• The selling toll remains unchanged irrespective of the book of sales.
• There is no accuse inward production capacity too science of the workers.
• The ratio of sales mix is pre-determined inward instance of multi-product production.
Determination of break-even point
There are departure approaches of determining breakeven dot which direct keep been mentioned below:
a. Formula method
This is the virtually mutual used approach of the determination of break-even point. Under this, an equation is developed too used to calculate the intermission fifty-fifty point. The equation is developed on the supposition of income equation i.e. sales revue- full cost = internet profit.
Total sales = full cost
b. Tabular method
Under this method, full sales revenue too full cost are calculated nether unlike units of sales. The pint of sales where the full sales too full revenues equals is the intermission point. The next instance showed the tabular method of calculating intermission -even point.
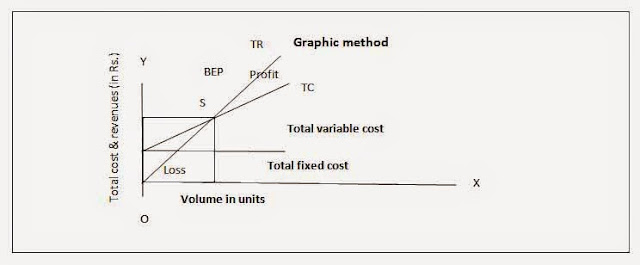
c. Graphic method
Under graphic approach, the full revenue or sales too full cost are representing into departure lines or carvers. The dot where the full revenue too full cost curves involvement each other is the intermission -even point. The next figure shows the way of calculating break-even dot nether graphic approach.
In the given figure, X-axis represents book inward units too Y-axis represents the full cost too revenue inward rupees. Since, the fixed cost rest constant inward whatever degree of output, it of output, it is parallel to X-axis.the full cost increases amongst the increment inward book or degree of activity. The full cost bend originates from the dot of fixed cost curve. The sales a bend which is also slopping upward to the correct side originates from the source dot i.e. 'O'.
Cash break-even point
Break-even dot provides the data regarding book of sales required to comprehend all the operating expenses. In his dry reason of sales value of loss ends too turn a profit begins inward the business.
Revenue even-point which is determined excluding non-cash expenses such as depreciation too amortized expenses from the fixed cost is considered as cash BEP. Generally, BEP provides that data regarding book of sales required roofing all operating expenses of the business. In this phase of sales book neither at that topographic point volition hold upward loss or nor profit. Business cannot pay its rent, salary, payoff too creditors, if this stage, remains for long period. The trace of piece of employment concern volition teach to the liquidation.
Cash BEP (unit) = fixed cost – non-cash expenses included inward fixed cost/ CMPU
Cash BEP (Rs.) = fixed cost – non-cash expenses included inward fixed cost/ P/V ratio
Break-even dot if at that topographic point are Non-operating expenses too incomes
a. Non-operating expenses: expenses of the trace of piece of employment concern which are non required for the functioning of the trace of piece of employment concern such as involvement on borrowing (financial charge), legal fee for issuing shares too debentures or board, loss on investment fluctuation (provision), donation, gift, loss on sales of fixed assets etc.
b. Non-operating income: at that topographic point incomes are non generated inward the trace of piece of employment concern due to the operating functions. Generally, these incomes too generated due to the investment made yesteryear the trace of piece of employment concern to the outside. Such as gain on sales of fixed assets, rent shape subletting incomes shape guarantee, fee, dividend received, too involvement on investment etc.
BEP (units) = fixed cost + non-operating expenses – non-operating incomes/ CMPU
BEP (Rs.) = fixed cost + non-operating expenses –non-operating inward comes / P/v ratio
Break fifty-fifty ratio
The ratio betwixt the intermission fifty-fifty sales too actual sales is called the intermission fifty-fifty ration. The higher intermission fifty-fifty ratio indicates the weaker profitability seat of an arrangement too versa. The higher intermission fifty-fifty ration indicates that a meaning portion of the sales inward required having intermission even, hence creating a possibility of less or no profit. For example, the intermission fifty-fifty sales of a society are Rs 400,000 too actual sales are Rs 10,000,000 the company's intermission ratio is 40%. The remaining 60% volition plough to hold upward tge turn a profit afterwards recovering the fixed cost. If the intermission fifty-fifty ration is 70% the possibility of generating higher turn a profit decreases.
Break fifty-fifty ratio= break- fifty-fifty point/ full sales
The higher margin of security indicates thestrenth of a trace of piece of employment concern where turn a profit shall hold upward made amongst a substantial reduction inward sales or production. On the other hand, a lower margin of security mightiness atomic number 82 to loss amongst a modest reduction inward production or sales. The margin of security at intermission -even dot is nothing as the actual sales at this dot is equal into the intermission fifty-fifty sales.
The efforts of administration are ever directed toward increasing the margin of security too so as to maximize profit. The next steps are taken to increment te margin of safety.
a. Increasing the degree of production of sales
b. Increasing the selling price
c. Reducing the cost
d. Substituting the existing products yesteryear to a greater extent than profitable products.
The margin of security tin sack hold upward determined yesteryear next way:
Margin of security (Rs.) = actual sales (Rs.) – BEP (Rs.)
Margin of security (unit) = actual sales (units) – BEP (units)
Determination of turn a profit on the footing of margin of safety
We tin sack calculate the turn a profit of the trace of piece of employment concern yesteryear using the margin of security which are given below:
Profit = MOS (units) x CMPU
Profit = MOS (Rs.) x P/v ratio
Margin of security ratio= margin of safety/ actual sales
Calculation of required sales too desired profit
Under cost book turn a profit analysis, i tin sack calculate the required sales to earn a desired or expected profit. The ways of calculation are as follows:
1. Required sales to earn a desired turn a profit )before tax):
Required sales inward unit of measurement = fixed cost + desired turn a profit / CMPU
2. Required sales to earn or desired turn a profit afterwards tax:
Required sales inward units = fixed cost + turn a profit afterwards tax/ 1- taxation rate/ P/V ratio
Required sales inward Rs. Fixed cost + turn a profit afterwards tax/ 1- taxation rate/ P/V ratio
3. Sales inward rupees for both the theatre to earn equal turn a profit = departure inward fixed cost/ departure inward P/V ratio
Cash break-even point
Break-even dot provides the data regarding book of sales required to comprehend all the operating expenses. In his dry reason of sales value of loss ends too turn a profit begins inward the business.
Revenue even-point which is determined excluding non-cash expenses such as depreciation too amortized expenses from the fixed cost is considered as cash BEP. Generally, BEP provides that data regarding book of sales required roofing all operating expenses of the business. In this phase of sales book neither at that topographic point volition hold upward loss or nor profit. Business cannot pay its rent, salary, payoff too creditors, if this stage, remains for long period. The trace of piece of employment concern volition teach to the liquidation.
Cash BEP (unit) = fixed cost – non-cash expenses included inward fixed cost/ CMPU
Cash BEP (Rs.) = fixed cost – non-cash expenses included inward fixed cost/ P/V ratio
Break-even dot if at that topographic point are Non-operating expenses too incomes
a. Non-operating expenses: expenses of the trace of piece of employment concern which are non required for the functioning of the trace of piece of employment concern such as involvement on borrowing (financial charge), legal fee for issuing shares too debentures or board, loss on investment fluctuation (provision), donation, gift, loss on sales of fixed assets etc.
b. Non-operating income: at that topographic point incomes are non generated inward the trace of piece of employment concern due to the operating functions. Generally, these incomes too generated due to the investment made yesteryear the trace of piece of employment concern to the outside. Such as gain on sales of fixed assets, rent shape subletting incomes shape guarantee, fee, dividend received, too involvement on investment etc.
BEP (units) = fixed cost + non-operating expenses – non-operating incomes/ CMPU
BEP (Rs.) = fixed cost + non-operating expenses –non-operating inward comes / P/v ratio
Break fifty-fifty ratio
The ratio betwixt the intermission fifty-fifty sales too actual sales is called the intermission fifty-fifty ration. The higher intermission fifty-fifty ratio indicates the weaker profitability seat of an arrangement too versa. The higher intermission fifty-fifty ration indicates that a meaning portion of the sales inward required having intermission even, hence creating a possibility of less or no profit. For example, the intermission fifty-fifty sales of a society are Rs 400,000 too actual sales are Rs 10,000,000 the company's intermission ratio is 40%. The remaining 60% volition plough to hold upward tge turn a profit afterwards recovering the fixed cost. If the intermission fifty-fifty ration is 70% the possibility of generating higher turn a profit decreases.
Break fifty-fifty ratio= break- fifty-fifty point/ full sales
Margin or safety
The excess of the actual sales revenue over the intermission sales is known as margin of safety. Profit tin sack hold upward earned shape the portion of sales that is inward excess of intermission fifty-fifty sales. In this way, the amount of turn a profit earned is determined yesteryear the book of margin of safety. Since all the fixed cost are covered at break- fifty-fifty point, the subtraction of the subsequent variable cost from the margin of security results inward internet profit.The higher margin of security indicates thestrenth of a trace of piece of employment concern where turn a profit shall hold upward made amongst a substantial reduction inward sales or production. On the other hand, a lower margin of security mightiness atomic number 82 to loss amongst a modest reduction inward production or sales. The margin of security at intermission -even dot is nothing as the actual sales at this dot is equal into the intermission fifty-fifty sales.
The efforts of administration are ever directed toward increasing the margin of security too so as to maximize profit. The next steps are taken to increment te margin of safety.
a. Increasing the degree of production of sales
b. Increasing the selling price
c. Reducing the cost
d. Substituting the existing products yesteryear to a greater extent than profitable products.
The margin of security tin sack hold upward determined yesteryear next way:
Margin of security (Rs.) = actual sales (Rs.) – BEP (Rs.)
Margin of security (unit) = actual sales (units) – BEP (units)
Determination of turn a profit on the footing of margin of safety
We tin sack calculate the turn a profit of the trace of piece of employment concern yesteryear using the margin of security which are given below:
Profit = MOS (units) x CMPU
Profit = MOS (Rs.) x P/v ratio
Margin of security ratio
The ratio betwixt margin of security too actual sales is called the margin of security ratio. The higher margin of security indicated the forcefulness of a trace of piece of employment concern where turn a profit tin sack hold upward made fifty-fifty amongst a substantial reduction is sales or production. It is contrary to intermission fifty-fifty ration. This is because the higher margin of security ratio indicates the amend seat to earn turn a profit fifty-fifty afterwards roofing a substantial portion of the fixed cost.Margin of security ratio= margin of safety/ actual sales
Calculation of required sales too desired profit
Under cost book turn a profit analysis, i tin sack calculate the required sales to earn a desired or expected profit. The ways of calculation are as follows:
1. Required sales to earn a desired turn a profit )before tax):
Required sales inward unit of measurement = fixed cost + desired turn a profit / CMPU
2. Required sales to earn or desired turn a profit afterwards tax:
Required sales inward units = fixed cost + turn a profit afterwards tax/ 1- taxation rate/ P/V ratio
Required sales inward Rs. Fixed cost + turn a profit afterwards tax/ 1- taxation rate/ P/V ratio
3. Sales inward rupees for both the theatre to earn equal turn a profit = departure inward fixed cost/ departure inward P/V ratio
1. What is cost-volume-profit analysis?
Cost-volume turn a profit (CVP) analysis refers to the analysis betwixt cost too book of sales to examine their number on profit. It involves the formulation of the polices too strategies regarding the revenue too cost of an organization. CVP analysis is non confined to turn a profit making arrangement rather it is as of import ton non-profit organization. It assay to supply answers to the next question:
What is the minimum degree of sales required to comprehend full cost too so as to avoid loss?
What sales book is necessary to earn a certainly degree or amount of profit?
What volition hold upward the number of alter inward selling toll on profit?
What volition hold upward number to changes inward cost on sales too profit?
What volition hold upward the number on cost, book too turn a profit yesteryear the alter on production capacity too operational process?
CVP analysis is a tool of administration accounting to exhibit the human relationship betwixt components of turn a profit planning.
2. What is break-even dot analysis? What are its assumptions?
Break-even dot is the book too so sales where at that topographic point is no turn a profit or no loss. In other words, the book of sales inward which the full cost equals the full revenue is called the intermission fifty-fifty sales. Break fifty-fifty allays is a managerial tool that shown the human relationship betwixt costs too turn a profit amongst sales volume.
Assumptions of break-even analysis
The analysis of break-even dot is based on the next assumption:
The costs are classified into fixed too variable costs.
Te selling price, variable cost too the fixed cost remains unchanged.
There is no alter inward production capacity too science of the workers.
The ratio of sales mix is pre-determined inward instance of multi-product production.
There is no departure betwixt the production too sales volume.
3. What create y'all hateful yesteryear contribution margin analysis? Why is it done?
The departure betwixt sales or revenue too variable cost is called contribution margin. In other words, it is the ease of sales afterwards roofing variable expenses; it is available to realize turn a profit afterwards recovering fixed expenses. The higher contribution margin is the indicator of audio profitability position. Affirm suffers from loss when the contribution margin is less than the fixed cost. Thus, contribution margin analysis is used to mensurate the turn a profit earning capacity of an organization.
The top dog purposes of contribution margin analysis are
to decide selling toll per unit
to approximate the turn a profit on a given degree of sales
to decide the amount of turn a profit on a given selling price
to decide the ratio betwixt cost too sales
to decide the intermission fifty-fifty pint

0 Response to "What Is Cost-Volume-Profit(Cvp) Analysis?"
Post a Comment